Geocentric
Members-
Posts
32 -
Joined
-
Last visited
Everything posted by Geocentric
-
In Clark's tables, atomic masses of certain isotopes has a number written as subscript. What is its significance?I have just completed my bachelors degree in Physics and don't know such a basic thing. Its really shameful, isn't it?Maybe I never thought about it.Somebody please help.
-
When 2 simple harmonic motions are applied to a particle at right angles to each other having time periods in the ratio 1:2, you get a figure of eight. When the phase difference is (pi)/4,3(pi)/4,... you don't get a perfect figure of eight.Can it be called a distorted eight or is there any other name? I would like to follow the nomenclature that is universally accepted.That is why I asking.Thanx in advance.
-
How do we define the principal section of a crystal--- A plane containing the optic axis and the poynting vector.Is there a better and simple way of defining it? Can it be defined as the plane containing the optic axis and the plane of incidence?
-
1)I have a basic doubt on polarization. It is given in book that the plane of polarization is perpendicular to the plane of vibration. What was need for defining the plane of polarization to be perpendicular to the plane of vibration? When I searched the internet, I found a site which says that the plane of polarization is the plane in which the magnetic field vector is oscillating and plane of vibration is the plane in which the electric field vector oscillates. In an electromagnetic wave, the electric field vector is perpendicular to the magnetic field vector. Though this sounds to be true, I would like have the opinion of this forum.
-
1) The curie temperature of iron is 1043 Kelvin. Assume that iron atoms, when in metallic form have moments of 2 Bohr magneton per atom. Iron is body centered cube with lattice parameter a = 0.286 nm. Calculate the curie constant. I solved it in the following way: Let m be the magnetic moment of an iron atom, let N be the number of atoms per unit volume, let K be the boltzmann constant, let mu be the permeability of free space and let C be the Curie constant. m = 2[m(:D] {where m(B) is Bohr magneton} = 18.54 x 10^(-24) A-m^2 N = n/(a^3) {where n is number of atoms in 1 cubic lattice of iron} = 2/[(0.286 x 10^(-9))^3] = 8.5 x 10^28 atoms per unit volume C = [(m^2)(mu)N]/[3K] C = 0.89 But the answer given in my book is 0.66. Someone good in solid state physics please help me!
-
# I have some doubts regarding achromatism of lenses: 1)If we want to form an achromatic combination of lenses in which both are made of same material, one should be convex and the other should be concave, isn’t it? Is there any other condition to be satisfied along with this? 2)It is given in a book that, a convex achromatic combination of 2 lenses of the same material placed some suitable distance is possible in the following cases: a)Both are convex b)Both cannot be concave c)Convex lens of greater focal length and concave lens of smaller focal length. Is it true? 3)A convex achromatic combination of 2 lenses of the same material placed in contact can be obtained using a convex lens of lower dispersive power and a concave lens of higher dispersive power. Is it true? 1)For the first question,I think the reason behind having one convex and other concave in order to form an achromatic doublet is that, they disperse the beam in opposite directions as one is converging and other is diverging. According to the condition for achromatism of lenses, w1/w2 = -f1/f2 as w1 & w2 are different, f1 & f2 should be different. Is it right? 2)For the second question, a) If both are made of same material, then their dispersive powers will be same. From the condition for achromatism of lenses, f1=-f2 If both are convex, then this is not possible, isn't it? :D Similarly both cannot be concave. c) Similarly this cannot be true. So for achromatism of 2 lenses made of same material placed in contact: # one should be convex and other should be concave. # Both should be of same focal length. 3) I think the third question is wrong because 2 lenses made of same material cannot have different dispersive powers. Please correct me if I am wrong.
-
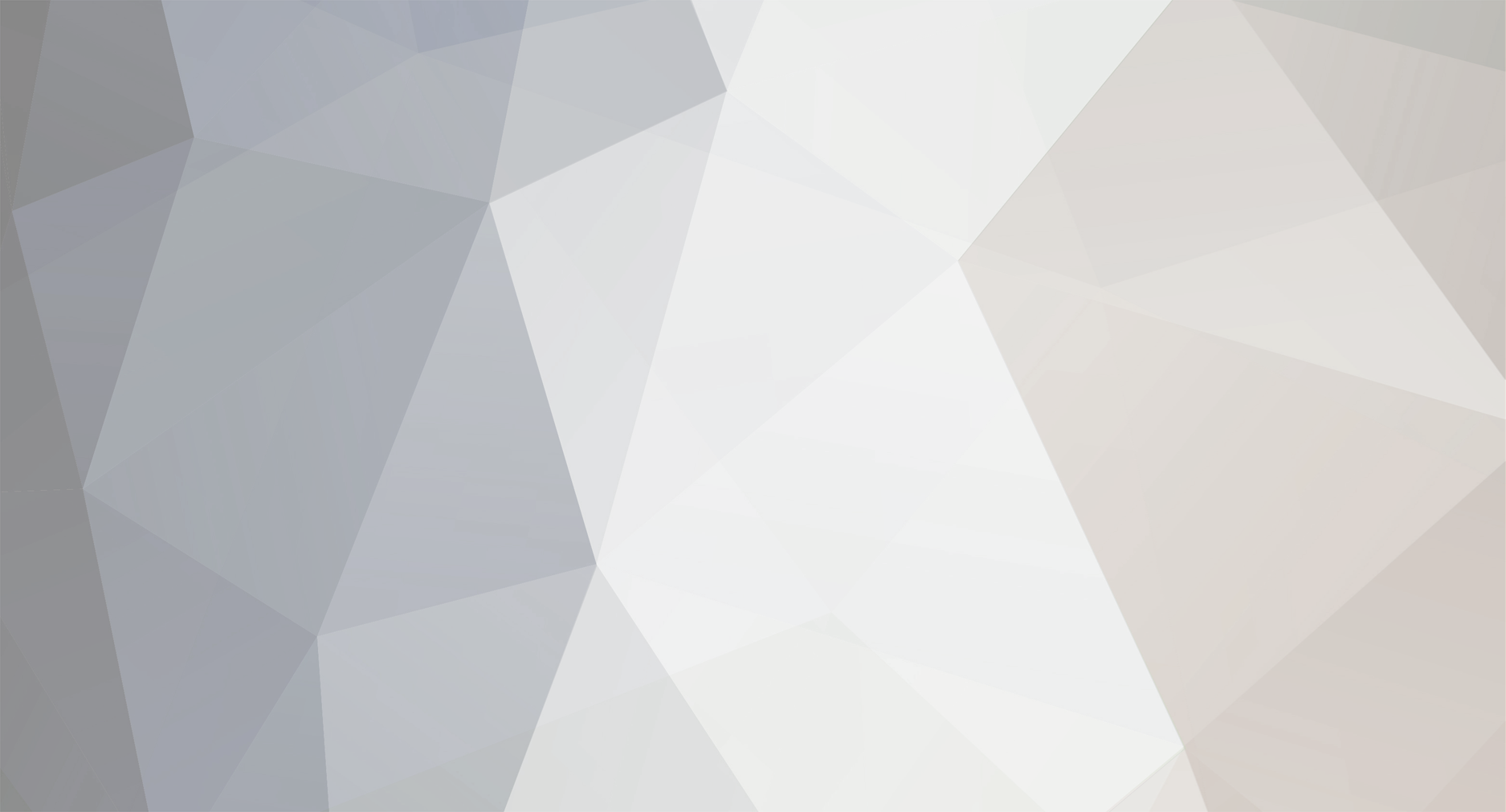
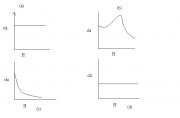
1)The variation of magnetic susceptibility(chi) with the magnetizing field for a paramagnetic material is given by which graph? For a paramagnetic material, the magnetic susceptibility(chi) is a constant and a small positive quantity. So the answer should be (d). But the answer given in my book is (a). Please guide me.
-
1)Two coils of self inductance 4 Henry and 16 Henry are wound on the same iron core. What is the coefficient of mutual inductance for them? Can anyone give an idea on how to go about this problem?
-
Spectrum produced by hydrogen atom
Geocentric replied to Geocentric's topic in Science Projects and Homework
Anyway, thanks for the guidance. -
Spectrum produced by hydrogen atom
Geocentric replied to Geocentric's topic in Science Projects and Homework
Yes. U mean that the radiation excites the hydrogen atom and is responsible for the production of emission spectrum of hydrogen. The action of the radiation is like the action of electric field in a discharge tube containing hydrogen gas. Since Balmer series lies in the visible region only that series will be visible. Am I right now?But it could have been in a better way. I can't believe you were a teacher! -
Spectrum produced by hydrogen atom
Geocentric replied to Geocentric's topic in Science Projects and Homework
Yes, my professors are open. But having studied spectroscopy during my first year, I find it bit embarassing to ask my professor now. So, i thought of taking the help of this forum. But i will not change my opinion-You r mean!!!:D -
Spectrum produced by hydrogen atom
Geocentric replied to Geocentric's topic in Science Projects and Homework
It may be easy for you but not for me as far as spectroscopy is concerned. Your are really harsh. I never expected such a reply. I am still in the learning stage. How do you expect me to have replied to queries of others? In the last 3 months I have posted just 13 questions out of 2000 questions I solved. Does that reflect that I don’t do any homework before posting? My foundations are weak in spectroscopy. So I thought that I would get help from the forum members. I asked this question with whatever little knowledge I had. Moreover, the questions that I have posted in the forum were not given as assignment in my college. I am trying to work the problems given in a book on my own. I feel solving a number of problems would help me to understand the subject well. -
# A continuous band of radiation having all wavelengths from about 1000 Angstrom to 10000 Angstrom is passed through a gas of monoatomic hydrogen. In the emission spectrum one can observe the entire: a)Lyman series b)Balmer series c)Paschen series d)Pfund series I didn’t understand the question. If the radiation containing wavelengths from 1000 Angstrom to 10000 Angstrom is passed through a gas of monoatomic hydrogen, isn’t that the absorption spectrum of hydrogen atom? If that is the case, then no spectrum will be produced because the series limit of Lyman, Balmer and Paschen series comes in the range from 1000 Angstrom to 10000 Angstrom and all these lines will be missing in the spectrum. Please correct me if I have wrongly understood the question.
-
# Neutrons bombard nuclei of N(14,7) converting it into Li(7,3). The process is accompanied by the emission of: 1)4 protons and 4 neutrons 2)6 protons and 2 electrons 3)1 alpha particle, 2 protons and 1 neutron 4)2 alpha particles and gamma ray photon I get 2 solutions here. N(14,7) + n(1,0) ---> Li(7,3) + 4p(1,1) + 4n(1,0) N(14,7) + n(1,0) ---> Li(7,3) + 2(alpha particles) + (gamma rays) Is it right? When N(14,7) is bombarded with a neutron, is the emission of 2 different set of particles possible? Here N=nitrogen, Li=Lithium, n=neutron, p=proton.
-
# In a perfectly elastic relativistic collision, which one of the following quantities is not conserved: a)Momentum b)Energy c)Rest mass d)Angular momentum In non relativistic elastic collisions, energy and momentum will be conserved. But I don’t know about relativistic elastic collisions. Could anyone please explain? Can we apply the Newtonian concepts in these cases? Suppose the collision is inelastic (relativistic), then which quantity will be conserved?
-
# According to De-Broglie, the waves are associated with: a)Moving charged particles only b)Moving neutral particles only c)Electrons only
-
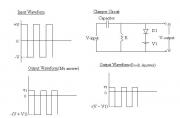
# Draw the output waveform for the following clamper circuit. Assume that 5y = 5RC >> T/2 where y = time constant of the RC circuit, T = time period of the input square wave voltage. I solved it in the following way: Positive half cycle of input voltage During positive half of input voltage when V=V1, D1 exists in forward biased condition. Hence, V-output = V1. Negative half cycle of input voltage During negative half cycle, D1 exists in reverse biased condition. Hence V-output = Potential difference across resistance R = (-V) + (-V) where one –V is due to the input voltage and the other –V is due to the charged capacitor. Hence V-output = -2V. But the difference between my output waveform and the output waveform given in my book is that in my book they have taken 2V downwards from V1 whereas I have taken it from the origin. As per the book answer, the output voltage at a time T/2 is (2V – V1). How can that be possible when an output voltage of -2V is obtained during the negative half cycle of input voltage? But in a clamper circuit, the output waveform has the same voltage swing as the input waveform. So, my answer is wrong but I don’t know where I have gone wrong. Could anyone please help me with this problem?
-
# Foucault’s experiment to measure the velocity of light supported: 1)Corpuscular theory 2)Wave theory 3)Photon theory 4)Electromagnetic wave theory It cannot be Corpuscular theory because it said that the velocity of light in a denser medium is greater than that in a rarer medium. It however supported wave theory as it said that the velocity of light in a denser medium is less than that in a rarer medium. But the experiment does not support photon theory because we do not consider the particle nature of light. But I don’t know whether it supported the Electromagnetic wave theory. Could anyone clear my doubt?
-
# It is said that the velocity of electromagnetic waves in a medium depends upon the mechanical and electrical properties of a medium. Is it true? But the expression to find the velocity of electromagnetic waves in a medium = 1/(M)(E) says that it depends upon the electrical & magnetic properties of a medium. Please clear my doubt. Here M = permeability of medium and E = Permittivity of medium.
-
Is there an expression to find the equivalent focal length of 3 lenses placed coaxially?
-
i am sorry, i typed it by mistake.
-
# Three convex lens of focal length 10 cm each are mounted coaxially as shown in figure. An object O is placed at a distance of 20 cm from L1 and the final image formed is at a distance of 20 cm from L3. What is the distance L1L2? Please help me with this problem. If the distance L2L3 was given this problem could be easily solved. But without that value, how to solve this problem?
-
Thats fine.